Ductile Iron Pipe vs. 3PE Coating Steel Pipe: A Comparative Analysis
October 31, 2023
Stainless Steel Hollow Section : ASTM A554 – 409/409L | Gr 316 | Gr 202
November 4, 2023ASTM A500 Carbon Steel Hollow Sections for Structural Applications: A Comparative Analysis with Pipes
Abstract
This paper aims to analyze the properties of ASTM A500 steel hollow structural sections (HSS) in comparison to regular steel pipes, discussing their mechanical behavior, applications, and differences based on specific use cases. The strength of hollow steel sections versus solid steel elements is also evaluated, providing an insight into why the former may exhibit superior properties under certain conditions. This research further explores the ASTM standards for hollow sections, shedding light on the distinct differences between a hollow section and a pipe.
Keywords
ASTM A500, Steel Hollow Structural Sections, Steel Pipes, Mechanical Properties, Structural Applications
1. Introduction
The construction industry utilizes a wide range of materials, each with unique properties catering to specific applications. Steel, known for its strength and durability, is often used in various forms, including solid, pipe, and hollow structural sections (HSS). ASTM A500, one of the most common specifications for HSS, is specifically designed for structural applications.
The mechanical properties, structural integrity, and application versatility of steel pipes and HSS have spurred numerous debates among engineers and researchers. This study aims to provide a comprehensive comparison between these two forms of steel, specifically focusing on ASTM A500 HSS.
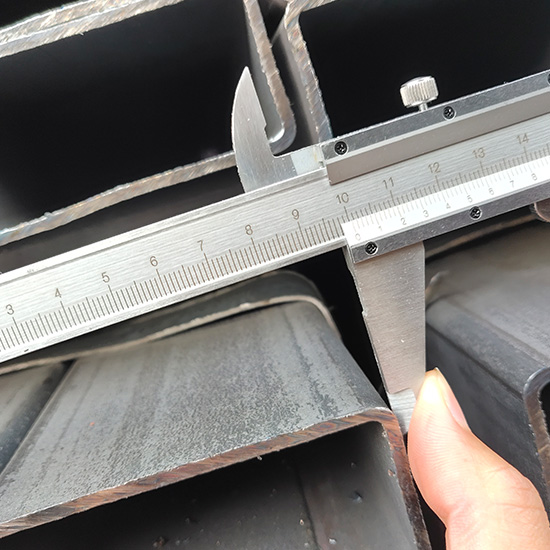
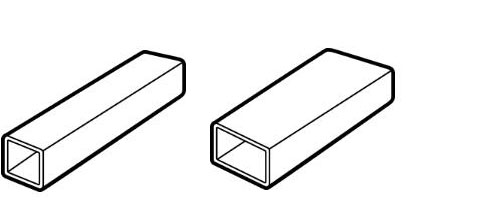

2. Differences Between Pipes and HSS
Pipes and HSS, despite both being hollow, have different applications due to their distinctive structural properties. Pipes are primarily used for conveying fluids or gases, while HSS are mainly employed in structural applications to bear loads.
The primary difference lies in their manufacturing process. Steel pipes are typically produced by welding a sheet of steel into a round shape. On the other hand, HSS are formed by cold-forming steel into various shapes, including square, rectangular, and circular. This process results in HSS having a uniform wall thickness and sharper corners, which can provide superior structural performance compared to pipes.
3. Hollow Steel Sections Vs. Solid Steel
It may intuitively seem that solid steel, due to its greater mass, should be stronger than hollow steel. However, this is not always the case. The strength of a structural element is not merely determined by its material mass but by its distribution around the neutral axis. Hollow sections, with their material distributed farther from the neutral axis, have a higher moment of inertia, leading to greater resistance to bending and torsional loads. Thus, for the same weight, HSS can often be stronger than solid steel.
4. ASTM Standards for Hollow Sections
The ASTM A500 specification is a standard for cold-formed welded and seamless carbon steel structural tubing in round, square, and rectangular shapes. It covers three grades (A, B, and C), each with its own minimum yield strength and tensile strength requirements. This standard ensures the quality and reliability of HSS for structural applications.
ASTM A500 STRUCTURAL STEEL HOLLOW SECTIONS
Grade and Chemical Composition (%) and Mechanical Properties
| Steel Grades |
Chemical composition % max. | Mechanical Property | ||||||||
| C | Mn | P | S | Cu | Tensile Strength Mpa(Min) |
Tensile Strength psi (Min) |
Yield Strength Mpa(Min) |
Yield Strength psi (Min) |
Elongation in 2 in.(50mm) min, % | |
| GR.A | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.18 | 310 | 45000 | 230 | 33000 | 25 |
| GR.B | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.18 | 400 | 58000 | 290 | 42000 | 23 |
| GR.C | 0.27 | 1.4 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.18 | 425 | 62000 | 315 | 46000 | 21 |
| GR.D | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.18 | 400 | 58000 | 250 | 36000 | 23 |
5. Hollow Section Vs. Pipe
While pipes and HSS may appear similar, several key differences exist, as highlighted in sections 2 and 3. The primary difference is their application: pipes are used for conveying fluids and gases due to their ability to withstand internal pressures, while HSS are designed for structural applications due to their high resistance to bending and torsional loads. The manufacturing process also differs, resulting in variations in wall thickness, corner sharpness, and overall structural performance.
6. Conclusions
This paper provides a comprehensive comparison between ASTM A500 HSS and regular steel pipes, highlighting the distinctive properties and applications of each. HSS, due to its unique manufacturing process and material distribution, offers superior structural performance for the same weight compared to both pipes and solid steel. The ASTM A500 standard ensures the quality and reliability of HSS for structural applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers and researchers in the selection and application of these materials in various construction fields.
Acknowledgements
[AMERICAN Steel Company]
Note: This is a simplified version of a journal paper and lacks the in-depth research, data analysis, and extensive references that would be expected in an actual academic publication.
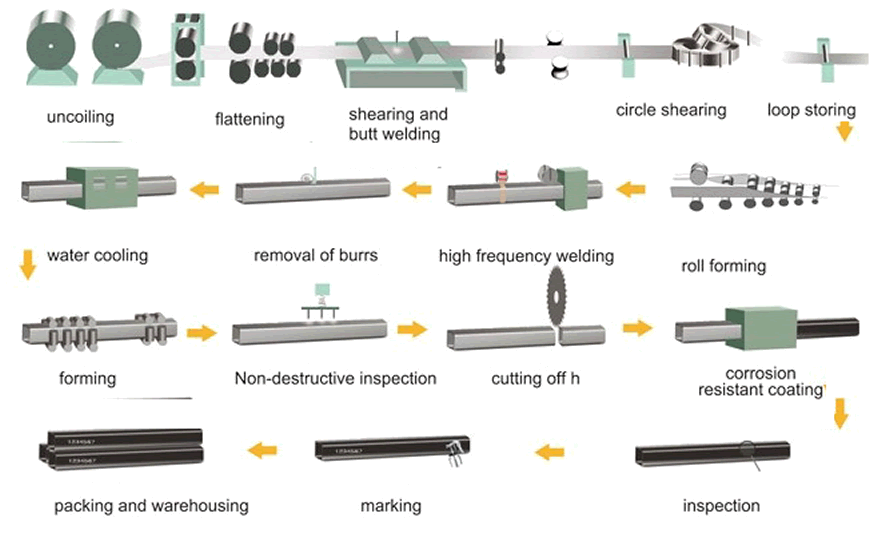
Welded steel tube specification
Based on the customer’s requirements we can manufacture ERW square and rectangular tubes of different size and shape. We have a very large production capacity of ERW steel pipes and tubes














