UNS N04401 Monel 401 Alloy Steel Tube
December 21, 2024
ASME SB622 Hastelloy C276 Nickel Alloy Seamless Steel Tube
January 1, 2025Comprehensive Outline: Butt Weld Seamless Steel Concentric and Eccentric Reducers
| Main Topics | Subtopics |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction | – Definition of butt weld seamless steel reducers – Importance in piping systems – Differences between concentric and eccentric reducers |
| 2. Understanding Butt Weld Fittings | – Overview of butt weld fittings – Manufacturing processes – Advantages of seamless over welded reducers |
| 3. Key Applications | – Use in industries like oil and gas, petrochemicals, power plants, and food processing – Specific examples and operational roles |
| 4. What Are Concentric Reducers? | – Design and geometry – Working principle – Typical applications |
| 5. What Are Eccentric Reducers? | – Design and geometry – Unique characteristics – Typical applications |
| 6. Material Composition | – Materials used in seamless steel reducers (e.g., carbon steel, stainless steel, alloys) – Properties required for performance under pressure and heat |
| 7. Manufacturing Process | – Hot forming vs. cold forming – Steps in seamless production – Inspection and quality control processes |
| 8. Standards and Specifications | – ASME, ANSI, DIN, and other standards – Dimensions and tolerances for concentric and eccentric reducers |
| 9. Installation of Butt Weld Reducers | – Step-by-step installation guide – Tools and equipment required – Welding techniques |
| 10. Concentric vs. Eccentric Reducers | – Key differences (design, usage, and flow characteristics) – Pros and cons of each type – Decision-making factors for selection |
| 11. Performance and Durability | – Resistance to pressure and temperature – Corrosion resistance and lifespan |
| 12. Benefits of Seamless Reducers | – Reduced risk of leakage – Smooth internal surfaces for efficient flow – Long-term cost-effectiveness |
| 13. Challenges and Limitations | – Cost factors – Installation challenges – Limitations in specific scenarios |
| 14. Emerging Trends and Innovations | – New materials and coatings for reducers – Advancements in manufacturing technologies |
| 15. Market Overview | – Global market analysis for seamless reducers – Key manufacturers and suppliers – Growth factors and future outlook |
| 16. FAQs | – Six FAQs addressing common queries about butt weld seamless steel concentric and eccentric reducers |
| 17. Conclusion | – Summary of the importance, applications, and benefits of seamless reducers – Final thoughts on selecting the right type for specific applications |
In-Depth Analysis: Butt Weld Seamless Steel Concentric and Eccentric Reducers
1. Introduction
Butt weld seamless steel reducers play a critical role in modern piping systems. These reducers are essential components used to connect pipes of different diameters, ensuring smooth and efficient flow within industrial systems. Seamless reducers are known for their reliability, durability, and resistance to pressure, making them indispensable in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation. Broadly, reducers are categorized into two types: concentric and eccentric, each serving unique purposes based on their design and functionality.
The key difference lies in their geometry. Concentric reducers have a symmetrical design where the centerlines of the inlet and outlet pipes align, while eccentric reducers feature an offset centerline, often used to prevent the pooling of fluids or gas.
2. Understanding Butt Weld Fittings
Butt weld fittings refer to pipe fittings that are welded directly to the pipe system, ensuring a robust, leak-proof connection. These fittings, including reducers, elbows, and tees, are essential for altering the pipe’s direction, diameter, or branching off.
Key Benefits of Butt Weld Fittings:
- Strength and Durability: Welded connections are stronger and more reliable than threaded or socket connections.
- Seamless Flow: The internal surface is smooth, minimizing turbulence and pressure loss.
- Wide Range of Sizes: Available in sizes ranging from a few millimeters to several meters in diameter.
3. Key Applications
Seamless reducers are used in a wide variety of industries, ensuring optimal flow and structural integrity in piping systems. Some of the key applications include:
| Industry | Specific Applications |
|---|---|
| Oil and Gas | Pipeline transportation, refining processes, offshore platforms |
| Petrochemicals | Chemical processing, fluid transfer systems |
| Power Generation | Cooling systems, boilers, and heat exchangers |
| Food Processing | Hygienic transfer of liquids and gases |
| Water Treatment | Distribution systems, desalination plants |
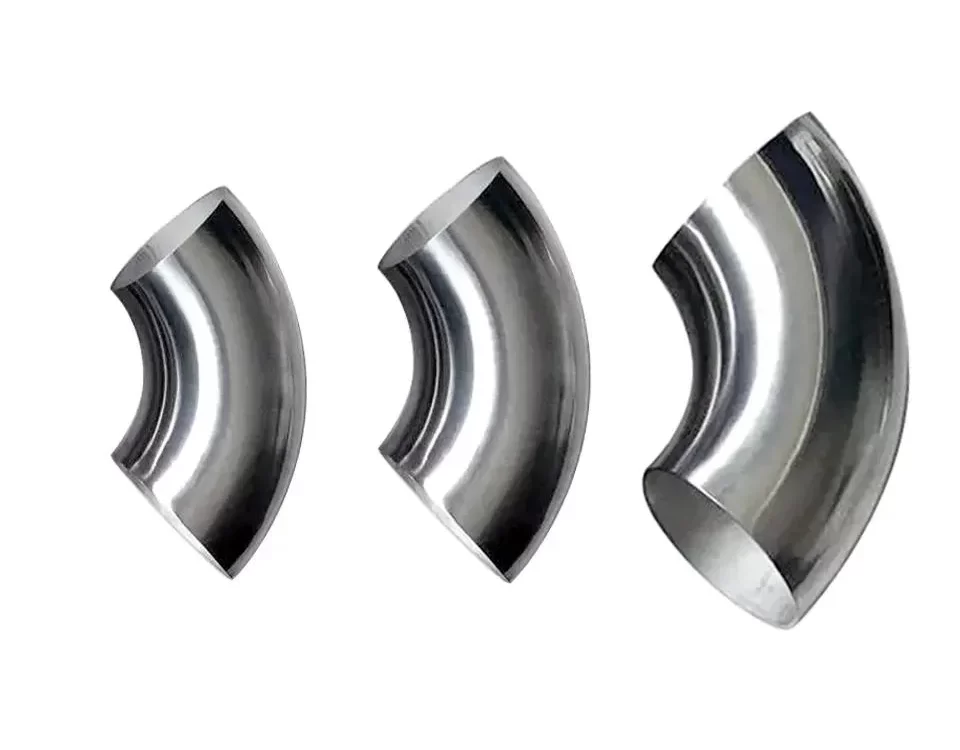
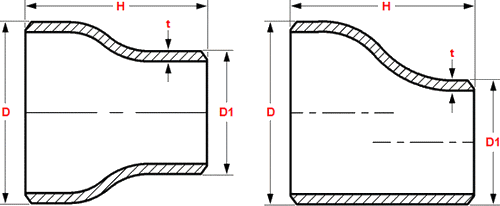
4. What Are Concentric Reducers?
Concentric reducers are designed with a symmetrical shape, where the centerlines of the inlet and outlet are aligned. This design ensures a smooth transition between pipes of different diameters, maintaining the integrity of the flow.
Features of Concentric Reducers:
- Design: Symmetrical cone-shaped structure.
- Flow Efficiency: Minimizes turbulence and pressure drop.
- Applications: Often used in vertical piping systems or where flow alignment is crucial.
5. What Are Eccentric Reducers?
Unlike concentric reducers, eccentric reducers have an offset design. This offset prevents the pooling of fluids, making them ideal for horizontal piping systems where the buildup of gas or liquid can create operational challenges.
Features of Eccentric Reducers:
- Design: One side of the reducer is flat, while the other tapers down.
- Flow Control: Ensures proper drainage and prevents air pockets.
- Applications: Commonly used in pump suction lines and horizontal pipelines.
6. Material Composition
The choice of material for seamless reducers depends on the application and operating conditions. Common materials include:
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High strength, cost-effective, suitable for high-pressure systems |
| Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for food processing and chemical industries |
| Alloy Steel | Enhanced resistance to heat and pressure, used in extreme environments |
7. Manufacturing Process
Seamless reducers are produced through advanced forming techniques to ensure uniformity and structural integrity. The steps typically involve:
- Material Selection: High-quality steel billets or tubes are chosen.
- Hot Forming: Steel is heated and shaped using molds or dies.
- Cold Forming: Additional shaping at room temperature for precision.
- Heat Treatment: Improves mechanical properties.
- Inspection: Dimensions and quality are verified using ultrasonic testing and radiography.
8. Standards and Specifications
Seamless reducers adhere to international standards to ensure compatibility and reliability in various systems. Key standards include:
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASME B16.9 | Factory-made wrought butt weld fittings |
| ANSI B16.25 | Butt weld ends |
| DIN 2616 | Reducers for welding |
9. Installation of Butt Weld Reducers
Proper installation ensures the reducer performs effectively. The process includes:
- Preparation: Ensure pipes and reducers are clean and free of debris.
- Alignment: Align the reducer with the pipe ends.
- Welding: Use appropriate welding techniques like TIG or MIG for seamless connections.
- Inspection: Check weld integrity using non-destructive testing methods.
10. Concentric vs. Eccentric Reducers
| Feature | Concentric Reducers | Eccentric Reducers |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Symmetrical | Offset |
| Applications | Vertical systems | Horizontal systems |
| Drainage | Not suitable for drainage | Ideal for preventing pooling |
| Common Usage | Vertical pumps, flow lines | Suction lines, horizontal pipelines |
11. Performance and Durability
Seamless reducers are engineered to withstand high pressure, temperature, and corrosive environments. Factors affecting performance include material composition, manufacturing process, and operating conditions.
12. Benefits of Seamless Reducers
- Leak-Free Connections: No welded joints ensure a tight seal.
- Enhanced Durability: Seamless construction improves strength.
- Cost-Effective: Long lifespan reduces maintenance costs.
13. Challenges and Limitations
- Cost: Seamless reducers are more expensive than welded ones.
- Manufacturing Complexity: Requires advanced techniques.
- Installation: Precision welding is critical for proper functioning.
14. Emerging Trends and Innovations
Advances in materials and manufacturing processes are making seamless reducers more efficient and durable. Examples include:
- Use of duplex stainless steel for improved corrosion resistance.
- Automation in forming processes for higher precision.
15. Market Overview
The global market for seamless reducers is driven by demand in industries like oil and gas. Key manufacturers include Vallourec, Sandvik, and Tubacex.
| Region | Market Share |
|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific | Dominates due to industrial growth in China and India |
| North America | Strong demand from oil and gas |
| Europe | Focus on high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials |
16. FAQs
- What is the difference between concentric and eccentric reducers?
Concentric reducers have aligned centerlines, while eccentric reducers are offset. - What materials are used for seamless reducers?
Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. - Why choose seamless over welded reducers?
Seamless reducers offer greater strength, durability, and resistance to leaks. - Where are eccentric reducers commonly used?
They are typically used in horizontal pipelines to prevent fluid pooling. - What standards govern seamless reducers?
Key standards include ASME B16.9 and DIN 2616. - Are seamless reducers suitable for high-temperature applications?
Yes, they are designed to withstand extreme pressure and temperature.
18. Comparison of Seamless vs. Welded Reducers
A critical distinction when choosing reducers is between seamless and welded types. Each has its own benefits and limitations depending on the application’s demands.
| Feature | Seamless Reducers | Welded Reducers |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Produced from a single piece of steel without any welds. | Manufactured by welding two or more pieces of steel. |
| Strength | Stronger due to the absence of weld joints. | Slightly weaker because weld joints are potential weak points. |
| Leak Resistance | Excellent, as there are no welds that could fail under pressure. | Moderate, depending on weld quality. |
| Durability | Higher, with superior performance under high-pressure conditions. | Lower, especially in extreme environments. |
| Cost | Higher due to complex manufacturing. | Lower due to simpler production processes. |
| Applications | High-pressure and high-temperature pipelines. | Low to medium-pressure applications. |
Seamless reducers are preferred for critical applications where reliability and durability are non-negotiable, while welded reducers are often used for less demanding environments where cost savings are a priority.
19. Importance of Surface Finish in Seamless Reducers
The surface finish of seamless reducers significantly affects their performance, especially in industries that require hygiene and precision, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. A smoother finish ensures:
- Reduced turbulence and friction within the pipeline.
- Prevention of debris accumulation or contamination.
- Easier cleaning and maintenance.
The typical surface finishes for seamless reducers include machined, polished, or electropolished finishes, depending on the application.
20. Troubleshooting Common Issues with Butt Weld Seamless Reducers
While seamless reducers are highly reliable, some issues may arise during their installation or operation. Here’s a look at common problems and their solutions:
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Improper fit during installation | Misalignment of pipes or reducers. | Ensure proper alignment and prepare surfaces. |
| Cracks or deformation | Poor welding or substandard material. | Use certified materials and trained welders. |
| Corrosion | Exposure to harsh chemicals or conditions. | Choose corrosion-resistant materials. |
| Leakage | Faulty weld joints. | Inspect welds thoroughly using NDT methods. |
Regular inspection and maintenance can prevent most of these issues.
21. Case Study: Application of Seamless Reducers in an Oil Refinery
In one notable instance, a large oil refinery in the Middle East upgraded its pipelines to include seamless concentric and eccentric reducers. The reducers played a vital role in:
- Managing high-pressure crude oil transfer.
- Ensuring proper drainage in horizontal pipelines to prevent fluid buildup.
- Enhancing operational efficiency by reducing turbulence and pressure drops.
The results showed a significant increase in pipeline performance, with reduced downtime and maintenance costs.
22. Factors to Consider When Selecting Butt Weld Seamless Reducers
Choosing the right reducer for your pipeline system involves evaluating several factors:
- Pipe Diameter: Ensure compatibility with existing pipes.
- Operating Pressure: Select materials capable of withstanding system pressures.
- Temperature: Choose materials that can handle high or low operating temperatures.
- Corrosion Resistance: For harsh environments, stainless steel or alloy steel is ideal.
- Flow Requirements: Decide between concentric and eccentric reducers based on fluid dynamics.
- Compliance: Ensure the reducer meets applicable standards (e.g., ASME, DIN).
23. Frequently Used Coatings for Seamless Reducers
To enhance performance, seamless reducers are often coated with materials that protect against corrosion, abrasion, and other environmental factors. Common coatings include:
- Epoxy Coating: Provides excellent corrosion resistance for water and wastewater pipelines.
- Galvanization: Offers protection against rust in outdoor and humid environments.
- Polyurethane Coating: High abrasion resistance, suitable for harsh industrial conditions.
Coating selection depends on the operating environment and desired longevity.
24. Cost Analysis: Seamless vs. Welded Reducers
| Cost Component | Seamless Reducers | Welded Reducers |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Material Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Manufacturing Cost | High due to advanced forming techniques. | Moderate, with simpler production. |
| Installation Cost | Similar for both, but seamless lasts longer. | Similar for both. |
| Maintenance Costs | Lower due to superior durability. | Higher due to potential weld failures. |
| Overall Cost-Effectiveness | High for critical applications. | Moderate, suitable for non-critical use. |
Although seamless reducers are initially more expensive, their longevity and reliability often result in lower total lifecycle costs.
25. Conclusion
Butt weld seamless steel concentric and eccentric reducers are indispensable in modern piping systems. Their ability to ensure smooth transitions between pipe diameters, maintain structural integrity under pressure, and resist corrosion makes them a preferred choice in industries ranging from oil and gas to food processing.
By understanding the differences between concentric and eccentric reducers, their applications, and the advantages of seamless construction, businesses can make informed decisions that optimize performance and reduce long-term costs. While the initial investment may be higher for seamless reducers, their reliability and durability justify the cost, especially in critical applications.
For a successful installation, always adhere to industry standards, select high-quality materials, and work with experienced professionals to ensure optimal performance.